Lewis Diagrams for Compound Formation The formation of many common compounds can be visualized with the use of Lewis symbols and Lewis diagrams. In a Lewis symbol, the inner closed shells of electrons can be considered as included in chemical symbol for the element, and the outer shell or valence electrons are represented by dots. Chemical Bonding Lewis dot structures, octet rule; ionic bonding model, covalent bonding model; covalent bond order, bond length, lone pairs; electronegativity and bond polarity, partial ionic character, metallic bonding (electron sea model) Binding forces (types; relationships to states, structure, properties; polarity.

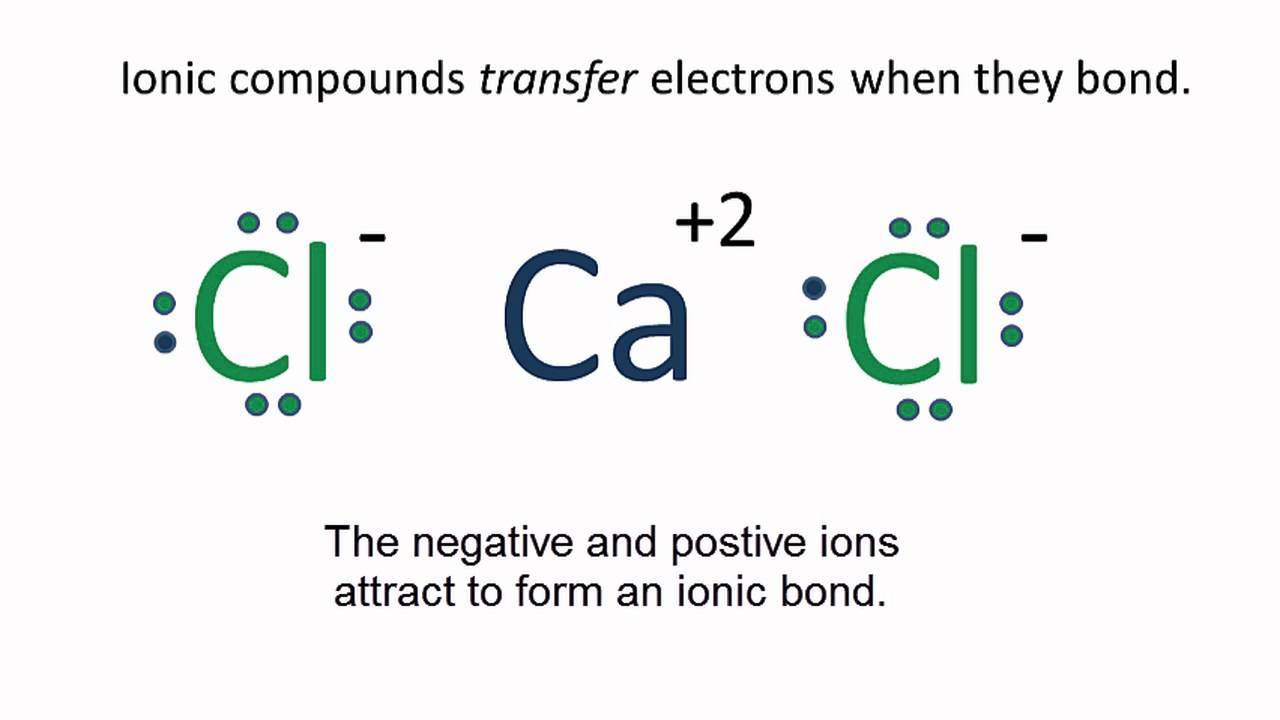
Lewis Structures are important to learn because they help us predict:
- the shape of a molecule.
- how the molecule might react with other molecules.
- the physical properties of the molecule (like boiling point, surface tension, etc.).

As a point of reference, the bond length in N2 is 109.8 pm. (c) In ionic azides, such as NaN3, the N–N bond lengths in the azide anion are equal; both are 116 pm. Draw a Lewis structure including all resonance structures and nonzero – formal charges for the isolated azide anion, N3 and explain why the bond lengths are equal in this. In 1916, ten years before the Schrodinger wave equation, G. Lewis suggested that a chemical bond involved sharing of electrons. He described what he called the cubical atom, because a cube has 8 corners, to represent the outer valence shell electrons which can be shared to create a bond.This was his octet rule. Rules for drawing Lewis dot structures. Figure 7.10 demonstrates the use of Lewis symbols to show the transfer of electrons during the formation of ionic compounds. Figure 7.10 Cations are formed when atoms lose electrons, represented by fewer Lewis dots, whereas anions are formed by atoms gaining electrons.
That helps us understand and predict interactions with things like medicine and our body, materials used to make buildings and airplanes, and all sorts of other substances. Lewis structures don't tell us everything, but along with molecule geometry and polarity they are hugely informative.
| Search 100+ Lewis Structures on our site. (Opens new window.) |
Click the Chemical Formula to see the Lewis Structure
| Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
Advanced Steps Notable Exceptions to the Octet Rule
|

Lewis Structures are important to learn because they help us predict:
- the shape of a molecule.
- how the molecule might react with other molecules.
- the physical properties of the molecule (like boiling point, surface tension, etc.).
As a point of reference, the bond length in N2 is 109.8 pm. (c) In ionic azides, such as NaN3, the N–N bond lengths in the azide anion are equal; both are 116 pm. Draw a Lewis structure including all resonance structures and nonzero – formal charges for the isolated azide anion, N3 and explain why the bond lengths are equal in this. In 1916, ten years before the Schrodinger wave equation, G. Lewis suggested that a chemical bond involved sharing of electrons. He described what he called the cubical atom, because a cube has 8 corners, to represent the outer valence shell electrons which can be shared to create a bond.This was his octet rule. Rules for drawing Lewis dot structures. Figure 7.10 demonstrates the use of Lewis symbols to show the transfer of electrons during the formation of ionic compounds. Figure 7.10 Cations are formed when atoms lose electrons, represented by fewer Lewis dots, whereas anions are formed by atoms gaining electrons.
That helps us understand and predict interactions with things like medicine and our body, materials used to make buildings and airplanes, and all sorts of other substances. Lewis structures don't tell us everything, but along with molecule geometry and polarity they are hugely informative.
| Search 100+ Lewis Structures on our site. (Opens new window.) |
Click the Chemical Formula to see the Lewis Structure
| Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
Advanced Steps Notable Exceptions to the Octet Rule
|
In 1916, ten years before the Schrodinger wave equation, G. N. Lewis suggested that a chemical bond involved sharing of electrons. He described what he called the cubical atom
, because a cube has 8 corners, to represent the outer valence shell electrons which can be shared to create a bond. This was his octet rule.
- Count the number of valence e- each atom brings into the molecule.For ions, the charge must be taken into account.
How many valence electrons in BeCl2?
How many valence electrons in NO2- and NO2+?
- Put electron pairs about each atom such that there are 8 electrons around each atom (octet rule), with the exception of H, which is only surrounded by 2 electrons. Sometimes it's necessary to form double and triple bonds. Only C, N, O, P and S (rarely Cl) will form multiple bonds.
Easeus data recovery pro free. Draw the Lewis dot structure for CF4.
The number of valence electrons is 4 + 4 ( 7 ) = 32 electrons.
So, we obtain:
Draw the Lewis dot structure for CO.
The number of valence electrons is 4 + 6 = 10 electrons or 5 pairs. Since both C and O allow multiple bonds we can still follow the octet and write:
- If there is not enough electrons to follow the octet rule, then the least electronegative atom is left short of electrons.
Draw the Lewis dot structure for BeF2.
In BeF2 number of valence e- = 2+ 2(7) = 16 e- or 8 pairs. Since neither Be or F form multiple bonds readily and Be is least electronegative we obtain:
- If there are too many electrons to follow the octet rule, then the extra electrons are placed on the central atom.
Draw the Lewis dot structure for SF4.
In SF4 the number of valence electrons is 6 + 4 ( 7 ) = 34 electrons or 17 pairs. Placing the extra electrons on S we obtain:
How can the octet rule be violated in this last example? The octet rule arises because the s and p orbitals can take on up to 8 electrons. However, once we reach the third row of elements in the periodic table we also have d-orbitals, and these orbitals help take the extra electrons. Note that you still need to know how the atoms are connected in a polyatomic molecule before using the Lewis-Dot structure rules.
Homework from Chemisty, The Central Science, 10th Ed.
Lewis Dot Structure For Ionic Compounds Calculator Compound
8.45, 8.47, 8.49, 8.51, 8.53, 8.55, 8.57, 8.59, 8.61, 8.63

